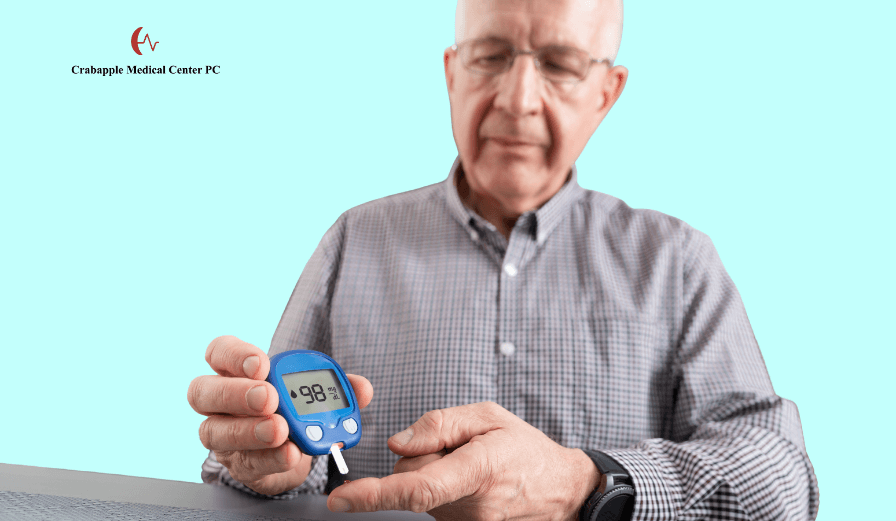
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide, including residents of Alpharetta, GA. Effective diabetes management requires a combination of regular monitoring, proper medication, and healthy lifestyle habits.
At Crabapple Medical Center, our team provides personalized care plans that empower patients to manage their condition confidently, reduce complications, and maintain a high quality of life.
This article explores practical strategies for diabetes care, including glucose monitoring, medication management, diet, physical activity, and ongoing preventive health measures.

Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes occurs when the body is unable to properly produce or utilize insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood glucose levels. There are three main types:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Typically diagnosed in children and young adults, it requires lifelong insulin therapy.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form, often associated with insulin resistance and lifestyle factors such as obesity and inactivity. It may be managed with oral medications, lifestyle modifications, and sometimes insulin.
- Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy and increases the risk of complications for both mother and child. Careful monitoring and management are essential to protect maternal and fetal health.
Understanding the type of diabetes you have is the first step toward effective disease management and long-term health.
The Importance of Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management. Consistently tracking blood sugar helps prevent complications, supports timely medical interventions, and enables patients to maintain optimal control over their condition.
By observing trends and fluctuations in glucose levels, both patients and healthcare providers can make informed decisions regarding diet, physical activity, and medication adjustments.
This proactive approach is essential for reducing the risk of long-term complications such as neuropathy, retinopathy, kidney disease, and cardiovascular problems.
Blood Glucose Monitoring Options
There are several methods available to monitor blood glucose, each offering unique benefits:
- Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG): This method involves using a glucometer to measure blood sugar at specific times throughout the day, such as fasting, pre-meal, and post-meal. SMBG provides immediate feedback and helps patients understand how lifestyle factors and medications impact glucose levels.

- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): CGM systems use a small sensor inserted under the skin to provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day. This technology allows patients to identify patterns, detect dangerous highs and lows, and respond quickly to fluctuations, enhancing overall disease management.
- HbA1c Testing: Unlike daily glucose checks, the HbA1c test measures average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. It is a critical indicator of long-term glucose control and helps providers evaluate the effectiveness of current treatment plans.
Frequency of Monitoring
The recommended frequency of blood glucose monitoring depends on factors such as diabetes type, treatment regimen, and individual health needs:
- Patients Using Insulin: Individuals on insulin therapy typically check their blood sugar multiple times per day to manage fluctuations and prevent hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
- Patients on Oral Medications: Those managing Type 2 diabetes with oral medications may require less frequent monitoring, though regular checks are still essential to assess treatment efficacy and maintain target glucose ranges.
- Special Circumstances: Illness, changes in diet or physical activity, pregnancy, or newly diagnosed diabetes may require more frequent monitoring to ensure safe and effective blood sugar management.
Medication Management for Diabetes
Proper medication management is crucial for maintaining stable blood glucose levels and preventing complications such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disease.
Common Diabetes Medications
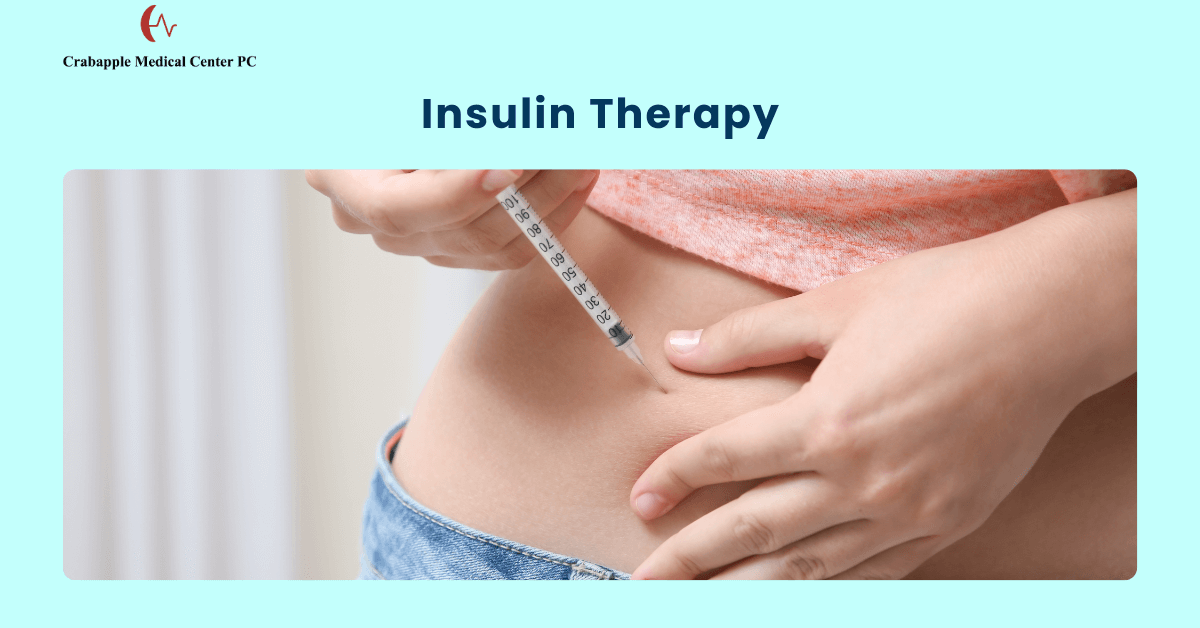
- Insulin Therapy: Required for Type 1 diabetes and sometimes for Type 2 diabetes. Available in various formulations, including rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulin.
- Oral Medications: Include metformin, sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors, and others. Each works differently to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce glucose production, or enhance insulin release.
- Non-Insulin Injectable Medications: Such as GLP-1 receptor agonists, which help regulate blood sugar and support weight management.
Tips for Effective Medication Use
Proper medication management is a critical component of diabetes care. Adhering to prescribed therapies ensures that blood glucose levels remain within target ranges, reduces the risk of complications, and enhances overall treatment effectiveness. Patients can take several proactive steps to maximize the benefits of their medications while minimizing potential risks.
1. Follow the Prescribed Schedule Precisely
Taking medications exactly as prescribed is essential for maintaining stable blood glucose levels. Skipping doses, taking extra doses, or altering the timing without guidance can lead to dangerous fluctuations, reduce treatment effectiveness, and increase the risk of complications such as hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
2. Monitor for Side Effects and Report Adverse Reactions Promptly
All medications carry the potential for side effects. Patients should be vigilant in observing changes in their body or new symptoms and communicate these promptly to their healthcare provider. Early reporting allows adjustments to be made safely, ensuring both efficacy and safety.
3. Coordinate with Your Healthcare Provider Before Combining Medications or Supplements
Many patients use additional medications, over-the-counter drugs, or dietary supplements. Before adding any new substance, consult your provider to avoid harmful interactions that could affect blood sugar control or overall health. This step is particularly important for diabetes medications, which can interact with a wide range of substances.
4. Maintain an Updated Medication List
Keeping an accurate and up-to-date list of all medications, dosages, and schedules is crucial. Bring this list to every appointment, including any changes or adjustments made by other healthcare providers. This practice ensures continuity of care, prevents errors, and allows your healthcare team to make informed decisions regarding your treatment plan.
By following these best practices, patients can optimize their diabetes medication regimen, maintain better glucose control, and significantly reduce the risk of complications.
Empower Your Health with Expert Diabetes Care
Effective diabetes management requires personalized guidance and consistent support. At Crabapple Medical Center in Alpharetta, GA, our team offers comprehensive care, from monitoring and medication to lifestyle strategies, helping you stay in control of your health. Book your appointment today and take charge of your diabetes journey.
Lifestyle Strategies for Diabetes Management
Lifestyle modifications are a cornerstone of diabetes care. Healthy habits can reduce dependence on medication, improve blood sugar control, and prevent complications.
Nutrition and Diet
- Focus on balanced meals rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
- Monitor carbohydrate intake to manage post-meal blood sugar spikes.
- Limit processed foods, sugary beverages, and excessive saturated fats.
- Consider meal planning or consulting a registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
Physical Activity
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Include strength training to improve insulin sensitivity and muscle mass.
- Start gradually if sedentary and gradually increase intensity under medical supervision.
Weight Management
- Maintaining a healthy weight can improve insulin sensitivity and overall blood sugar control.
- Small, consistent lifestyle changes are often more sustainable than drastic measures.
Stress Management
- Chronic stress can affect blood sugar levels. Practices such as meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or counseling can help manage stress effectively.
Sleep and Rest
- Adequate sleep supports hormone regulation, energy balance, and blood sugar control.
- Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep each night.
Preventing Complications Through Regular Check-Ups
Diabetes can lead to long-term complications affecting the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and cardiovascular system. Regular preventive care and screenings are essential to detect early changes and intervene promptly.
Key Preventive Measures
- Eye Exams: Annual dilated eye exams to detect diabetic retinopathy.
- Kidney Function Tests: Regular urine and blood tests to monitor kidney health.
- Foot Exams: Detects neuropathy and prevents ulcers or infections.
- Cardiovascular Assessments: Blood pressure, cholesterol, and heart health monitoring.
By adhering to recommended preventive measures, patients can significantly reduce the risk of complications and maintain independence and quality of life.
Diabetes Care at Crabapple Medical Center in Alpharetta, GA
At Crabapple Medical Center, our approach to diabetes care combines advanced monitoring technologies, personalized medication management, and practical lifestyle guidance. Our dedicated team works closely with patients to create individualized care plans, educate them on effective disease management, and provide ongoing support.
Patients benefit from:
- Comprehensive evaluations and screenings
- Individualized medication adjustments
- Nutrition and lifestyle counseling
- Continuous education and support for self-management
- Coordinated care for comorbid conditions
Our goal is to empower patients to take control of their diabetes, prevent complications, and achieve long-term wellness.
Tips for Patients Newly Diagnosed with Diabetes
Receiving a diabetes diagnosis can feel overwhelming, but with the right guidance and proactive strategies, patients can take control of their health and maintain a high quality of life. At Crabapple Medical Center in Alpharetta, GA, our team supports newly diagnosed patients with education, resources, and personalized care plans. The following tips can help you navigate the early stages of diabetes management effectively:
1. Educate Yourself About Your Condition and Treatment Options
Understanding the type of diabetes you have, how it affects your body, and the available treatment options is essential. Knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions, follow your care plan accurately, and recognize early warning signs of complications.
2. Establish a Consistent Monitoring Routine
Regular blood glucose monitoring is key to effective management. Work with your healthcare provider to develop a schedule that fits your lifestyle, including routine checks for fasting, pre-meal, and post-meal blood sugar levels. Consistent monitoring helps identify patterns and allows timely adjustments to your care plan.
3. Learn to Read Nutrition Labels and Plan Balanced Meals
Diet plays a central role in diabetes management. Understanding how to read food labels, track carbohydrate intake, and make healthy choices can help maintain stable blood sugar levels. Focus on nutrient-rich foods such as vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats while minimizing processed foods and sugary drinks.
4. Incorporate Physical Activity Into Your Daily Schedule
Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity, supports weight management, and enhances overall well-being. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week, including activities like walking, swimming, or cycling, and add strength training exercises to build muscle and support glucose control.
5. Communicate Openly With Your Healthcare Provider
Your healthcare team is your partner in diabetes management. Share challenges, ask questions, and provide updates about your progress. Open communication ensures your treatment plan remains effective and tailored to your needs.
6. Join Support Groups or Educational Programs
Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide encouragement, accountability, and practical tips for daily management. Educational programs offered by healthcare providers or community organizations can enhance your understanding and boost confidence in managing diabetes.
By following these steps, newly diagnosed patients can build a solid foundation for long-term diabetes management, prevent complications, and maintain a healthy, active lifestyle.
Take Control of Your Diabetes Today
Managing diabetes is a lifelong journey that requires commitment, education, and collaboration with healthcare professionals. By combining regular monitoring, proper medication, healthy lifestyle choices, and preventive care, patients can effectively control their blood sugar, reduce the risk of complications, and maintain a high quality of life.
At Crabapple Medical Center in Alpharetta, GA, we are committed to guiding patients every step of the way, providing comprehensive care, education, and personalized support. Schedule your consultation today and take the first step toward effective diabetes management and long-term wellness.
Partner With Crabapple Medical Center for Lifelong Wellness
Your health is our priority. With comprehensive monitoring, medication management, and lifestyle guidance, our team ensures you have the tools and support needed to manage diabetes successfully. Contact us now to book your appointment and take the first step toward a healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should I Check My Blood Sugar?
The frequency of blood glucose monitoring depends on your type of diabetes, treatment plan, and individual risk factors. Your healthcare provider will create a schedule tailored to your needs.
Can Lifestyle Changes Reduce My Need For Medication?
Yes. Healthy eating, regular physical activity, weight management, and stress reduction can improve blood sugar control, sometimes reducing reliance on medications under your provider’s supervision.
Is Insulin Required For Type 2 Diabetes?
Not always. Many Type 2 diabetes patients manage their condition with lifestyle changes and oral medications, but insulin may be necessary if blood sugar remains uncontrolled.
How can I Prevent Diabetes if I’m At Risk?
Lifestyle modifications, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and routine screenings, can significantly lower your risk of developing diabetes.
Can Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Replace Fingerstick tests?
CGM provides real-time glucose readings and trends, which can reduce the need for frequent fingerstick tests. However, occasional fingerstick tests may still be recommended to verify accuracy.